The ozone layer plays a vital role in safeguarding life on Earth. It screens out much of the sun’s harmful UV radiation. On this International Day for the Preservation of the Ozone Layer, on 16 September, a focus point is the Montreal Protocol. The day recognizes the broader impact the Montreal Protocol has on climate change. Moreover, there is a need to keep acting in collaboration, forge partnerships, and develop global cooperation to tackle climate challenges.
The Montreal Protocol

In 1994, the UN General Assembly proclaimed 16 September the International Day for the Preservation of the Ozone Layer, commemorating the date when the Montreal Protocol was signed in 1987. This was the first international treaty that was signed by all countries of the world. It is considered one of the greatest environmental success stories.
The chart below shows the decreasing consumption of ozone-depleting substances covered by the Montreal Protocol.
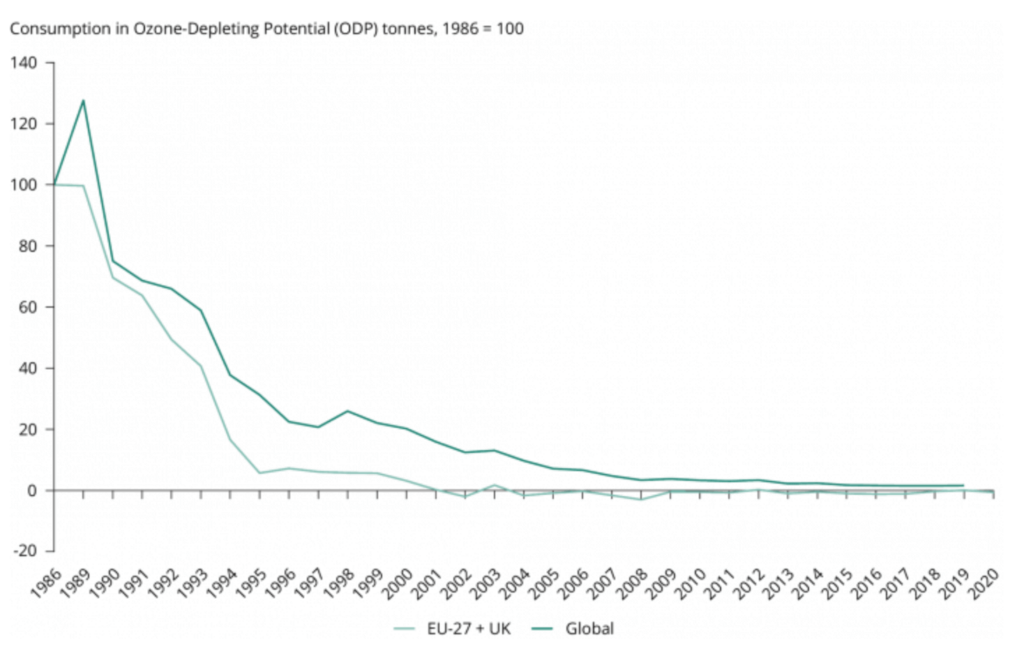
The Montreal Protocol’s objective is to cut down the production and consumption of ozone-depleting substances in order to reduce their presence in the atmosphere and thus protect the Earth’s ozone layer.
When the world found out that ozone-depleting gasses used in aerosols and cooling were creating a hole in the sky, the world came together—using global cooperation to phase out these ozone-depleting gasses with the Montreal Protocol.
The importance of Earth’s ozone layer

The ozone layer is a natural layer of gas in the upper atmosphere. It protects humans and other living things from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. Although ozone is present in small concentrations throughout the atmosphere, most (around 90%) exists in the stratosphere, a layer 10 to 50 kilometers above the Earth’s surface. The ozone layer filters out most of the sun’s harmful UV radiation and is crucial to life on Earth.
Because of the Montreal Protocol, the ozone layer is healing. But much remains to be done to ensure the continued recovery of the ozone layer. Regulation and reduction of ozone-depleting substances need to be continually prioritized to protect the ozone layer and our Earth’s climate.
Ozone-depleting gases and substances are responsible for the formation of what we call the ozone hole. This can be observed in satellite images of the Antarctic ozone layer. The depletion of the ozone layer leads to higher levels of harmful UV radiation reaching the Earth’s surface. The negative consequences include an increase in specific types of skin cancers, the development of eye cataracts, and the weakening of the immune system. Additionally, UV radiation has detrimental effects on both land-based ecosystems. Especially those in water, causing changes in growth patterns, food chains, and biochemical processes.
It’s worth noting that many human-made substances that deplete the ozone layer are also potent greenhouse gases. Some of these substances can have a global warming impact up to 14,000 times stronger than carbon dioxide (CO2). Carbon dioxide is the primary greenhouse gas responsible for climate change.
Thanks for reading along!
With this blog post, we want to raise awareness about how important it is to take care of the ozone layer. More than that, the importance of supporting the Montreal Protocol and protecting Life on Earth.
Don’t forget to check out our blog for more content and tips about traveling and much more! Click here to visit now.
You can also subscribe to our newsletter to get exclusive tips and content.
